Harnessing the sun’s power to light up your garden is eco-friendly and a fantastic DIY project for beginners. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through building a solar-powered LED garden light circuit that automatically turns on at dusk and switches off at dawn. With a few electronic components and simple steps, you can create your sustainable lighting system that saves energy and reduces electricity bills.
Why Build a Solar-Powered Garden Light?
Solar-powered garden lights are an excellent choice for anyone who wants to add aesthetic lighting to their outdoor spaces without increasing energy costs. This DIY project is ideal for beginners because it uses easy-to-find components and involves basic electronics skills. With this setup, your lights will automatically turn on at night and turn off during the day, thanks to the solar panel and light-dependent resistor (LDR).
Components Required for the Solar LED Garden Light Circuit
To build this solar-powered garden light, you will need the following components:
- 6V Solar Panel
- NiCd Rechargeable Battery 600ma (AA)
- Schottky Diode (1N5817)
- Transistors: C9014, C9015, C9013
- Light Dependent Resistor (LDR1)
- Inductor (82µH)
- Resistors: 220kΩ, 10kΩ, 91kΩ, 100kΩ, 560Ω, 3.3Ω (2×)
- Capacitors: 100nF, 1nF, 300pF
- LEDs: 2× high-brightness LEDs
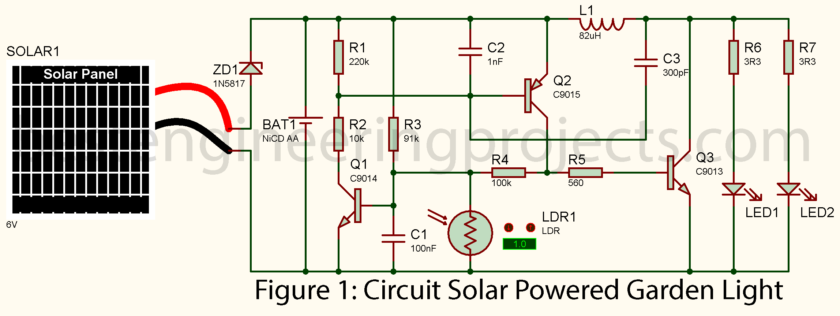
Circuit Diagram and Explanation
Below is the circuit diagram for your solar-powered LED garden light. The solar panel charges the battery during the day, and the LDR detects when it’s dark, activating the LEDs to illuminate your garden.
How the Solar Powered LED Garden Light Circuit Works
This circuit works by storing solar energy during the day and using it to power LEDs at night. Let’s break it down:
- Solar Panel Charges the Battery: BAT1 is a NiCd AA battery charged by the 6V solar panel during daylight. The 1N5817 Schottky diode prevents BAT1 from discharging back into the solar panel whenever there is no sunlight. This diode prevents current from flowing back toward the solar panel from the battery.
- LDR Light Detection: It uses a light-dependent resistor, LDR1, for ambient light level detection. During the day, the LDR resistance lowers, keeping the circuit in “charging” mode. The LDR’s resistance increases at night or when it darkens, triggering the transistors to turn on the LEDs.
- Automatic LED Lighting at Night: When the LDR detects low light levels (nighttime), the transistors (Q1, Q2, and Q3) switch on and allow the current to flow from the battery to the LEDs, lighting up your garden. The resistors R1, R3, R4, and R5 control the current flow and ensure that the LEDs light up only when necessary.
- Voltage Boost for Bright LEDs: The L1 inductor and the capacitors C2 and C3 ensure that voltage boosting is done to values high enough to drive the LEDs efficiently. This ensures that your garden is well-lit, even at night when the battery’s voltage output is low.
Assembling the Solar LED Garden Light
Follow these simple steps to assemble your solar-powered LED garden light:
- Solar Panel and Battery Connection: The ‘+’ terminal of the Solar Panel is to be connected to the anode of the 1N5817 (Schottky diode). The cathode of the diode is to be connected to the ‘+’ terminal of the NiCd battery, BAT1, and hence, proper daytime charging will be done.
- LDR Circuit Assembly: The LDR1 is in series with R2 as a 10kΩ resistor voltage divider, which detects ambient light level again. Thus, this will control the base of the first transistor, Q1, when the LEDs should turn on.
- Transistor Switching Circuit: Wire the transistors: Q1 as C9014, Q2 as C9015 and Q3 as C9013. These normally behave like electronic switches that turn on the LEDs depending on the response of the LDR. The resistors used to bias the transistors correctly are R1 220kΩ, R3 91kΩ, R4 100kΩ and R5 560Ω.
- Connect the inductor and Capacitor: Now, connect the inductor L1 of 82µH in parallel with the LEDs and the battery. Now, further add capacitors C2 and C3 to step up the voltage in order for LEDs to get enough power to stay on throughout the night.
- LED Connection Completion: LEDs LED1 and LED2 are connected in parallel, each with a respective current limiting resistors R6 and R7 to save them from the excessive current, which may cause damage.
Testing Your Solar-Powered Garden Light Circuit
When all is wired together, it is time to test the circuit:
-
Day Test: Place the solar panel in direct sunlight and measure the voltage across the battery terminals to ensure the battery is charging.
- Night Test: Cover the LDR or place the circuit in a completely dark area. By default, the LEDs will light because the LDR detects darkness.
If your circuit is working as expected, congratulations! You’ve successfully built a solar-powered LED garden light.
Advantages of a Solar-Powered LED Garden Light
-
Energy Efficiency: This is an ecologically friendly circuit since it uses renewable, free solar power.
-
Cost-Effective: It saves you money since you are not dependent on conventional electricity. The materials involved in making this circuit are cheap, and the rechargeable battery will save even more money.
-
Automatic Operation: The LDR and transistors switch automatically without the need for manual operation.
-
Simplicity: It is so simple to make this circuit- even a beginner enthusiast can easily make it. That makes this project a perfect starting point when working with DIY solar electronics.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- LEDs Not Turning On at Night: Check the connections around the LDR and the transistors. Ensure the LDR is positioned correctly and the biasing resistors are in place.
- Battery Not Charging: Ensure the solar panel receives sufficient sunlight and the diode is oriented correctly to prevent reverse currents.
- Dim LEDs: Verify that the inductor and capacitors are connected correctly to boost the voltage, and check the battery’s charge level.
Conclusion
This solar-powered LED garden light circuitry is the best DIY project for freshers interested in working with solar energy and electronics due to its simple, inexpensive, and environmentally friendly construction. Follow all the steps presented here, and a completely functional automatic lighting system will brighten your garden by utilizing the sun’s power.
By using renewable energy, you will save money on electricity and contribute to a greener future. Feel free to experiment with any size solar panel or LED configuration, whichever suits you best. Happy building!
Here are 5 similar projects from bestengineeringprojects.com with links:
- Automatic Street Light Control Using Solar Power
Automate street lights with solar energy, perfect for scaling up the garden light concept. - Solar Battery Charger Circuit for 12V Battery
Learn to charge a 12V battery using solar power, similar to the garden light’s charging mechanism. - Automatic LED Emergency Light Circuit
Build an emergency LED light that automatically switches on during power outages. - Automatic Night Lamp Using LEDs and LDR
A simple light automation project using LEDs and an LDR, similar to the garden light’s night sensor.
Very informative